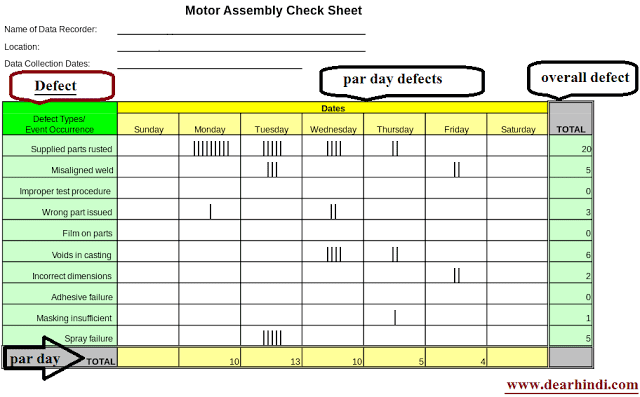
 Views
Views
These tools are known as '7 New Management and Planning Tools' and used by Six Sigma professionals for qualitative data analysis. This video gives you a brief introduction of all New 7 QC Tools.
28,160
From Embeds
Number of Embeds
ActionsDownloads
Comments
Likes
7 Qc Tools Pdf 2017
Embeds 0
New 7 Qc Tools Quality Management
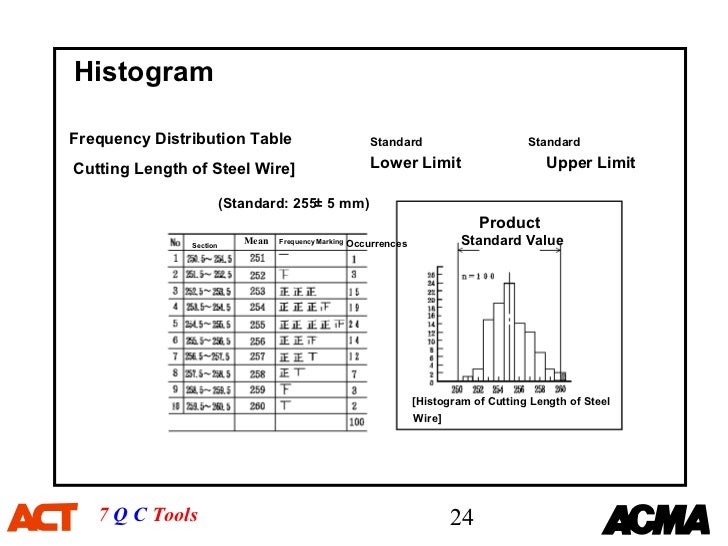
7 Qc Tools Pdf
-
-
New 7 QC Tools
History of the New 7 QC Tools Slide 1 0f 2
Committee* of J.U.S.E. - 1972 Aim was to develop more QC techniques with design approach Work in conjunction with original Basic Seven Tools New set of methods (N7) - 1977
-
-1
-
-
History of the New 7 QC Tools Slide 2 0f 2
!'
#
$
% &'( ( $
*##
+,
- .
/) ' 52
7 ,22 -%$3 $4 + + 2 3. 5 $ , 5-%$. 2. & ' & ( (, 6 3 $ 7 5 $ %
- 6
- 6 7 ,22 6 # + + 6 , 6 '
%&
-%$ 6
-%$ 2 & 6 ' )
3+ $ 2 3.-%$ .8 ,22 (Design Approach) #5
.5
4
#
- 96
TQM
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction What are the New 7 QC Tools? Affinity Diagrams Relations Diagrams Tree Diagrams Matrix Diagrams Arrow Diagrams Process Decision Program Charts Matrix Data Analysis
-
-2
-
-
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction What are the Basic 7 QC Tools ? Flow Charts
Run Charts Histograms Pareto Diagrams Cause and Effect Diagrams Scatter Diagrams Control Charts
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction '! ' # # .J9
$ #
#
*
.J9
The Basic 7 Tools •(
*
% 6
*
The New 7 Tools • ( • %
'
()
& Source: Nayatani, Y., The Seven New QC Tools (Tokyo, Japan, 3A Corporation, 1984)
-
-3
-
-
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction
5-Gen ' (
+,-.
Genba Genbutsu Genjisu Genri Gensoku
/
,' !' ' 012, ,/ $ # 3 4 $
# )# ( -5+ (#*-
# -
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction
# # /
/6 !' ,7 $' ($ 7 7 %
,
!
' *
8 - * -
# !' % #
-
# # #
-
/$
/6 $ (Sample) , ( $ 8 - * (Population) ,
'
-4
-
-
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction # $ $ *
- , , () /7 ) )
#
$ (Continuous)
(Discrete)
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction
/$ ,1: (
/6
%
# , (
!' (#* # 3
,2: * #,
% *
/$, # (#*
$,
-
-5
-
-
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction # , -9 - *: # 1 * % / $ Accuracy ( Relevant $ - * ! Timeliness $ #
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction
$/- *
!
(#*$ $ )# * )#$ * $ $ ' 3 , '*
-
# 8'*$ ' (#*$ , - *:
#
* 7
8 #
, $/- * ; *$ % # 3 7--2 $'6
-6
-
-
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction
% $
%
*7 - 7 $ ,
#* #
6
!
' - * # '* ! / % 7* )# 7 '% ( - * # ' * , $ '* % ( # , 7
#
'
! #7' &6 1
, #($
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction (
$ % -5+ - () KJ - () IR - () - () - () )
- ()
-
*'
$(#* , 7 $ < *
() (#* - () PDPC
$/- *
%
( 7
# $
$
:$7-
# &
-7
-
-
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction
-5+ ($ $ 7
,
36 '
,
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction
-5+ $ ,
,'$
( '
,
,
( 7 7# $$ '$
$7 / # ) # #
-
7
#
3
-8
-
-
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction
() ) # : (Affinity Diagram) =
:
Dr. Jiro kawakita % -5+ / , ' (#* ' % ( ( ( -9
# ( :
(Chaotic Situation) $7 (Concept Design)
-
New 7 QC Tools
History of the New 7 QC Tools Slide 1 0f 2
Committee* of J.U.S.E. - 1972 Aim was to develop more QC techniques with design approach Work in conjunction with original Basic Seven Tools New set of methods (N7) - 1977
-
-1
-
-
History of the New 7 QC Tools Slide 2 0f 2
!'
#
$
% &'( ( $
*##
+,
- .
/) ' 52
7 ,22 -%$3 $4 + + 2 3. 5 $ , 5-%$. 2. & ' & ( (, 6 3 $ 7 5 $ %
- 6
- 6 7 ,22 6 # + + 6 , 6 '
%&
-%$ 6
-%$ 2 & 6 ' )
3+ $ 2 3.-%$ .8 ,22 (Design Approach) #5
.5
4
#
- 96
TQM
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction What are the New 7 QC Tools? Affinity Diagrams Relations Diagrams Tree Diagrams Matrix Diagrams Arrow Diagrams Process Decision Program Charts Matrix Data Analysis
-
-2
-
-
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction What are the Basic 7 QC Tools ? Flow Charts
Run Charts Histograms Pareto Diagrams Cause and Effect Diagrams Scatter Diagrams Control Charts
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction '! ' # # .J9
$ #
#
*
.J9
The Basic 7 Tools •(
*
% 6
*
The New 7 Tools • ( • %
'
()
& Source: Nayatani, Y., The Seven New QC Tools (Tokyo, Japan, 3A Corporation, 1984)
-
-3
-
-
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction
5-Gen ' (
+,-.
Genba Genbutsu Genjisu Genri Gensoku
/
,' !' ' 012, ,/ $ # 3 4 $
# )# ( -5+ (#*-
# -
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction
# # /
/6 !' ,7 $' ($ 7 7 %
,
!
' *
8 - * -
# !' % #
-
# # #
-
/$
/6 $ (Sample) , ( $ 8 - * (Population) ,
'
-4
-
-
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction # $ $ *
- , , () /7 ) )
#
$ (Continuous)
(Discrete)
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction
/$ ,1: (
/6
%
# , (
!' (#* # 3
,2: * #,
% *
/$, # (#*
$,
-
-5
-
-
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction # , -9 - *: # 1 * % / $ Accuracy ( Relevant $ - * ! Timeliness $ #
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction
$/- *
!
(#*$ $ )# * )#$ * $ $ ' 3 , '*
-
# 8'*$ ' (#*$ , - *:
#
* 7
8 #
, $/- * ; *$ % # 3 7--2 $'6
-6
-
-
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction
% $
%
*7 - 7 $ ,
#* #
6
!
' - * # '* ! / % 7* )# 7 '% ( - * # ' * , $ '* % ( # , 7
#
'
! #7' &6 1
, #($
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction (
$ % -5+ - () KJ - () IR - () - () - () )
- ()
-
*'
$(#* , 7 $ < *
() (#* - () PDPC
$/- *
%
( 7
# $
$
:$7-
# &
-7
-
-
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction
-5+ ($ $ 7
,
36 '
,
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction
-5+ $ ,
,'$
( '
,
,
( 7 7# $$ '$
$7 / # ) # #
-
7
#
3
-8
-
-
New 7 QC Tools : Part I - Introduction
() ) # : (Affinity Diagram) =
:
Dr. Jiro kawakita % -5+ / , ' (#* ' % ( ( ( -9
# ( :
(Chaotic Situation) $7 (Concept Design)